4 Business Analysis Techniques for IT-Managers
February 6, 2017 / Estimated reading time: 5 minutes

Any project begins with a detailed study, references, monitoring and analysis. Before creating a project brief, a business analyst needs to answer a lot of questions about how to start communication with a customer, how to conduct an interview or how to find out the customer’s requirements. One more important question is how to choose the best business process analysis technique.
In this article, we will try to describe how to start working with customers and what business analysis techniques can be used to study the details before you start your project.
Here you will find basic info about:
- H-method;
- MoSCoW prioritization method;
- SQUARE methodology for working with the requirements for safety systems;
- CATWOE business analysis technique.
Where is the starting point?
You may ask “How to start a project from a scratch?” Whichever method for business analysis you choose, it will be associated with some of the following techniques:
- Definition of acceptance criteria and evaluation
- Brainstorming
- Business rules analysis
- Data glossary
- Diagrams of data flows
- Data modeling
- Analysis of decision-making
- Documents analysis
- Interviews
- Metrics and key performance indicators
- Analysis of non-functional requirements
- Tracking problems
- Process modeling
- etc.
So let’s start with the first popular business analysis technique.
H-method
What is H-method?
H-method is a simple technique that helps to gather business requirements. With its help, managers and business analysts can interview users and collect details.
The diagram “H” helps to overcome the problem of translation the way business users see the world into an IT context.
How H-method works
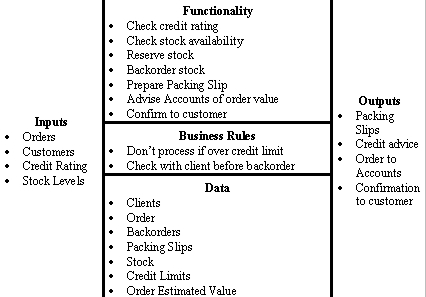
A grid of information is a background of any business analysis interview. The grid generates “H” hence. That’s why this business analysis technique has got such name. It includes 5 elements:
- Inputs – what people need to do.
- Functionality – what a person does.
- Business rules – what rules control the way of the person’s work.
- Data – the places and things the person needs to keep track.
- Outputs – what the person produces.
From the business perspective, users tell the business analyst the following:
- What do other people give you?
- What do you do?
- What rules are applied?
- What do you need to keep track of?
- What do you give other people?
You may explain your user that you are going to record information according to H-model. Specify what type of information will go into each space.
By the way, you do not need any tools such as timelines-services or Gantt charts at this stage of planning (you will need all these tools later, right after the analysis).
It’s easy to visualize your “H” evaluation diagram with a simple whiteboard where information can be jotted down.
Try to define the business processes prior to the work being undertaken, it will help you to plan and schedule your future project clearly.
The example:
- Inputs – A receipt for electricity payment for a month, a sum of money.
- Functionality – The required amount is credited to the cash account. Then it is transferred to the account of the company that provides electricity.
- Business rules – A bank commission is 2%. You can use only the national currency.
- Data – The number of the company’s account, the billing address.
- Outputs – The payment document.

MoSCoW technique
If you want to prioritize your business issues – one of the easiest methods for requirement prioritization is MoSCoW business analysis technique.
According to MoSCoW prioritization method, you can categorize your list of requirements into the following groups:
- M = must have. The requirements that must be satisfied in the final solution. The project will fail without these requirements.
- S = should have. A high-priority feature that is not critical to launch. But it is considered to be important and of a high value to users.
- C = could have. Requirements that are desirable but not necessary.
- W = won’t have. Requirements that can be delayed and may be included in a future stage of development.

SQUARE methodology
Apart of business rules and functional requirements, you may also need to find non-functional requirements. For example, security requirements.
SQUARE business analysis technique will help to do it easily. It will ensure the timely inclusion of safety requirements and related tasks in a project.
This business environment analysis technique aims to analyze and identify safety requirements in the early stages of project development.
It consists of 9 basic steps:
- Alignment meanings of the terms that will be used to describe the security requirements.
- Definition of security objectives.
- Creation artifacts that describe the security requirements.
- Assessment of the risks of different security threats.
- Choosing a technique for requirements gathering.
- Gathering requirements.
- Dividing all requirements into categories.
- Requirements prioritization.
- Verification and review.

CATWOE analysis
How to solve business issues with the help of CATWOE analysis?
This type of business analysis methods and techniques can be used to define the system or processes through highlighting their roots that involve converting the inputs into outputs.
The method includes 6 elements:
- Clients – the users of the system or process. CATWOE helps to understand how the process or system will affect them.
- Actors – the people who take part in the implementation of the changes in the system or process.
- Transformation – any changes that the system or process brings.
- Worldview – the big picture and the wider impact of the transformed system or process.
- Owner – the person with the power to control the system. He decides whether this system will be implemented or not.
- Environmental constraints – the restrictions that may halt operating of the system.

The business analysis technique is selected. What next?
Business analysis is only the beginning of a long and successful way of your project. Now you can prepare your project briefs and start to plan and schedule all the tasks.
If you still have not decided which projects planning tools to choose – GanttPRO is able to do everything for you.
Just have a look how it is easy to schedule projects with Gantt Charts:
What do you think about all these business analysis tools and techniques? Would you like to try any that seems new? Please share your opinion.